
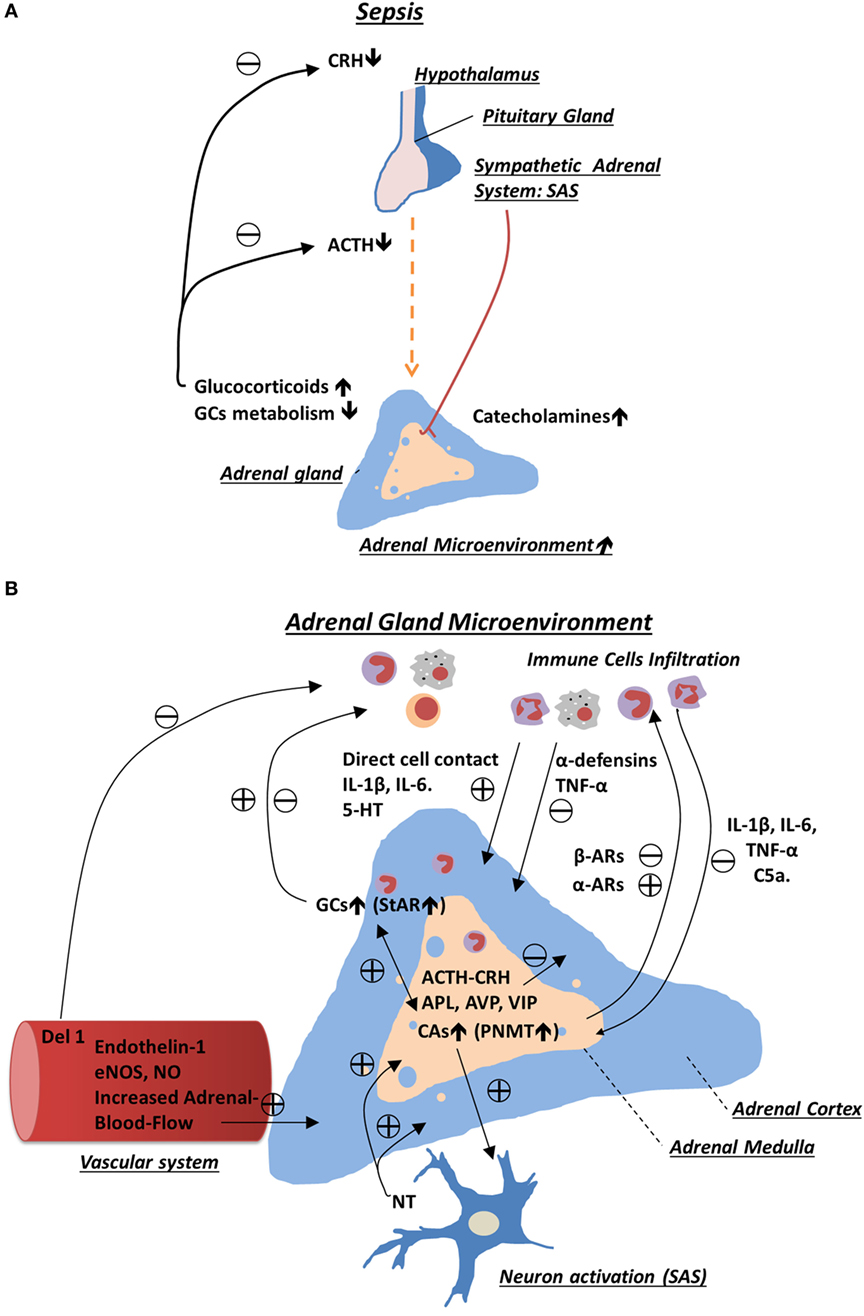
The HPA axis is a major neuroendocrine system that controls reactions to stress and regulates many body processes, including digestion, the immune system, mood and emotions, sexuality, and energy storage and expenditure. These organs and their interactions constitute the HPA axis.
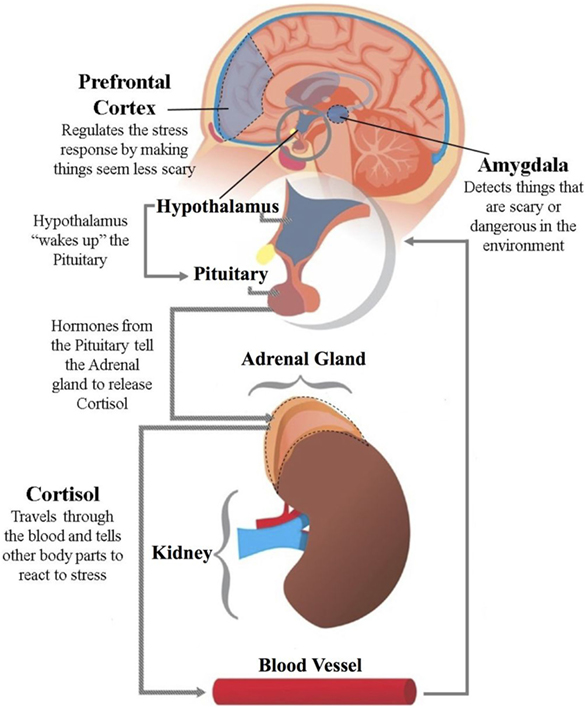
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis ( HPA axis or HTPA axis) is a complex set of direct influences and feedback interactions among three components: the hypothalamus (a part of the brain located below the thalamus), the pituitary gland (a pea-shaped structure located below the hypothalamus), and the adrenal (also called "suprarenal") glands (small, conical organs on top of the kidneys). Hypothalamus, pituitary gland and adrenal cortex


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
